ORCID (Open Researcher and Contributor ID) provides a unique identifier for researchers and scholars, allowing them to maintain a record of their scholarly activities and affiliations. ORCID is an open, non-profit, community-driven organization that aims to solve the name ambiguity problem in scholarly research and improve the discoverability of research outputs.
Follow these steps to use ORCID:
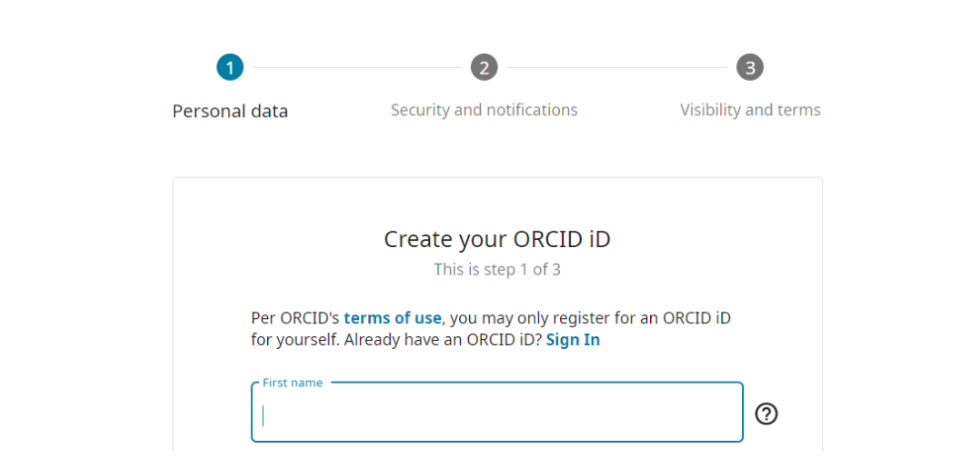
Step 1: Create an ORCID profile
The first step is to create an ORCID profile at orcid.org. This will allow you to register your unique identifier and manage your record.
Step 2: Add your information
Once you have created your ORCID profile, you can add your personal information, such as your name, affiliation, education, and employment history.
Step 3: Connect your works
You can link your ORCID profile to your research outputs, such as publications, datasets, and patents. You can do this by using one of the many ORCID integrations available, including citation managers, publishing platforms, and grant submission systems.
Ways for adding work to your record:
– Direct import your work from other systems to ORCID, such as:
- ResearcherID
- Scopus Author ID
– Import and export works via BibTeX: Import data from Google Scholar profile or EndNote to a BibTeX (.bib) file, then into your ORCID record. BibTeX is a platform for bibliographic citations.
– Add works manually
Step 4: Share your ORCID iD
Your ORCID iD is a unique identifier that can be shared with publishers, funders, and other research organizations. Sharing your ORCID iD will enable them to connect your research outputs to your record, reducing the chance of name ambiguity and ensuring that you receive credit for your work.

The ORCID iD is a 16-digit number that is compatible with the ISO Standard (ISO 27729), also known as the International Standard Name Identifier (ISNI), e.g https://orcid.org/0000-0002-9646-3055. Your ORICD iD is fully owned and controlled by you.
Step 5: Keep your record up to date
It is important to keep your ORCID record up to date, including your personal information and research outputs. This will ensure that your record accurately reflects your scholarly activities and affiliations, making it easier for others to discover your work.